In metal product design, the choice of forming method affects not only aesthetics and function but also feasibility and cost. Each process has its own strengths and limitations. By selecting the right method for your product, you can showcase design details while ensuring stable lead times and cost-effective production.
This article outlines common techniques with application examples to guide you toward the best option for your project.
Thickness & Tolerance Range by Forming Method
| Method | Applicable Thickness | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Etching | 0.1 ~ 1.0 mm |
+-0.03-0.2mm (for ≤0.5 mm thick) |
| Stamping | 0.3 ~ 2.0 mm | +-0.1mm |
| Hand Cutting | 0.3 ~ 2.0 mm | +-1.0mm |
| Laser Cutting | ≥1.0 mm | +-0.2mm |
Note: Greater thickness generally leads to higher tolerance and more visible cut edges.
Forming Techniques & Suggested Applications
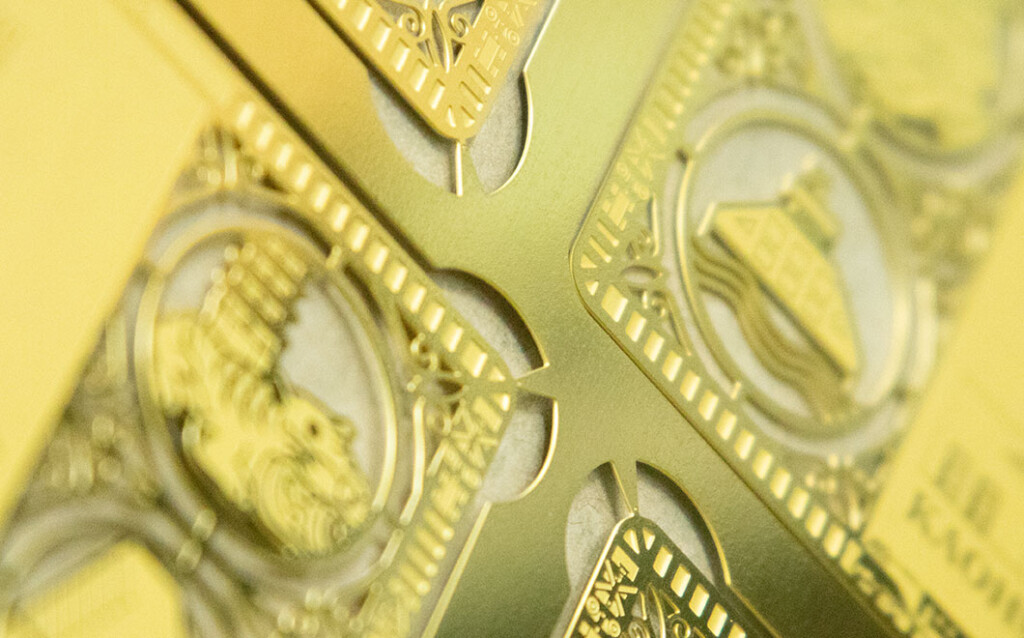

Etching
● Features
- Ideal for fine patterns, intricate cut-outs, and versatile shapes.
- Requires film/plate setup.
● Recommended Applications
Bookmarks, clips, art stencils, delicate ornaments, filters, spacers, models, and fixtures.Stamping (Punching)
● Features
- Best for simple shapes or holes, especially in mass production.
- Can be combined with adhesive backing.
- Stamping Die Required; some standard dies are available for renting to save costs.
● Recommended Applications
High-volume production of nameplates, badges, keychains.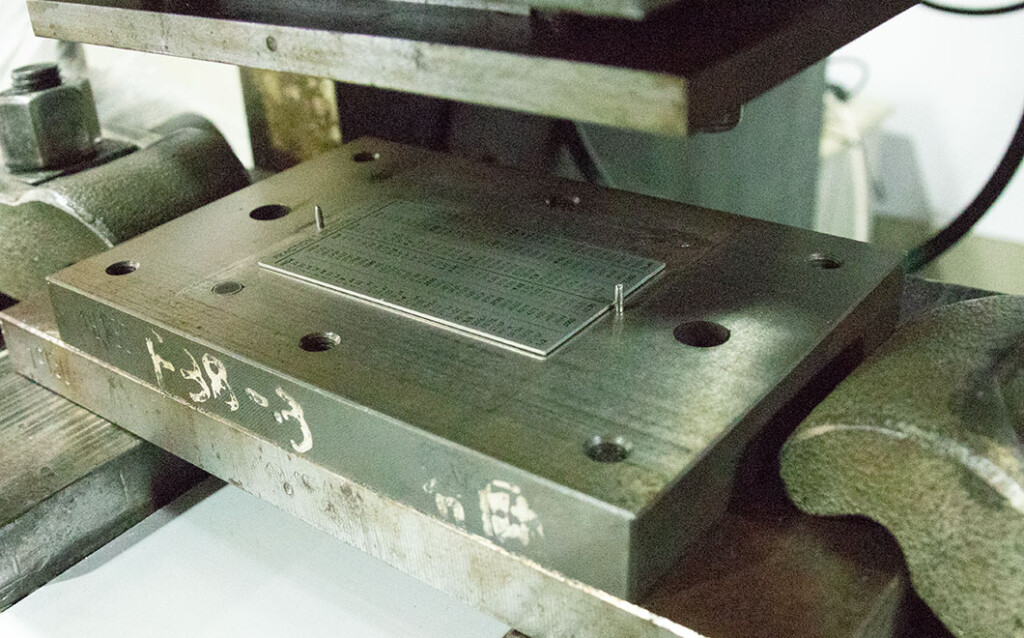
Stamping Die Comparison: Simple Die vs. Standard Die
| Item | Simple Die | Standard Die |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Basic alignment, larger tolerance | Higher precision, stable dimensions |
| Product Quality | More likely to produce burrs | Clean, sharp edges |
| Durability | Fewer strokes | More strokes |
| Cost | Lower tooling cost | Higher tooling cost |
| Best For | One-time or low-quantity needs | Long-term, high-volume, or high-stability production |

Hand Cutting
● Features
- Suitable for simple, straight-line shapes.
- Existing corner-rounding or hole dies can be used to refine edges or add round holes.
● Recommended Applications
Small-batch production of nameplates, and signs.Laser Cutting
● Features
- Suitable for large objects or small-batch production with irregular shapes or inner hole designs.
- For products requiring alignment, cumulative positioning error must be considered.
● Recommended Applications
Large nameplates, panels, staff gauges, thick components with irregular shapes.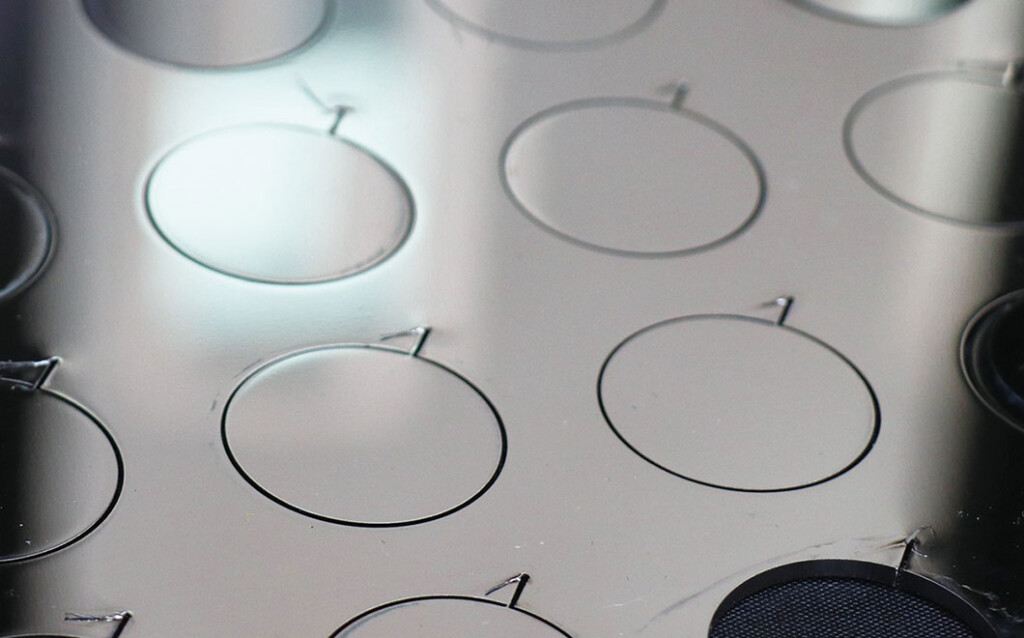
Summary of Recommendations
| Design Requirement | Recommended Method |
|---|---|
| Fine patterns, detailed cut-outs, small or large batches | Etching |
| Simple shapes/holes, high-volume with stable dimensions | Stamping |
| Straightforward lines, low-cost, small batches with larger tolerance | Hand Cutting |
| Thick material, large size, irregular shapes, small batches | Laser Cutting |
Need Expert Advice?
Share your design drawings with us, and we’ll provide process recommendations and feasibility analysis to help you create metal pieces that balance both beauty and quality.